Slide
Our Services

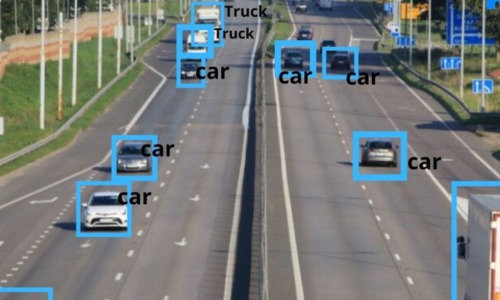
Classified Turning Movement Count
Optimizing traffic signal timings based on the observed traffic patterns to improve traffic flow and reduce congestion. Evaluating the safety and efficiency of an intersection design and identifying potential improvements. Understanding traffic demands to plan for future infrastructure projects and transportation improvements.
Link Count / ATR Count/Mid Blok Count
A Link Count involves collecting traffic data on a specific roadway link or segment, typically between two intersections or key points. The objective is to measure the volume of traffic passing through that specific segment. Link Counts help transportation planners and engineers understand traffic demand on various road sections, which is vital for capacity analysis, road maintenance, and infrastructure planning.
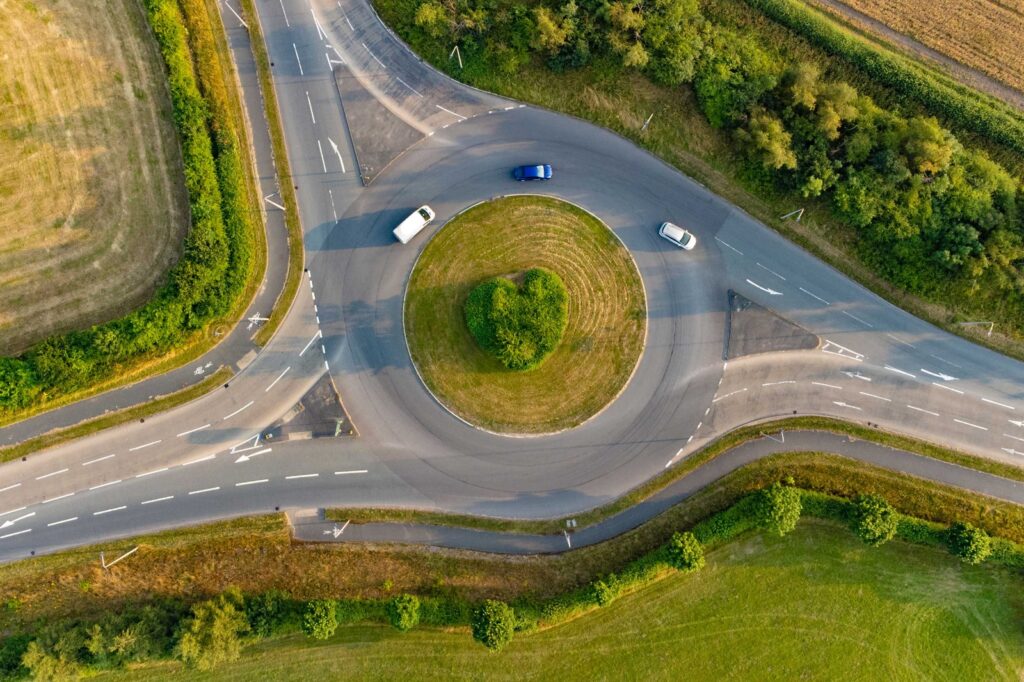


Round About Count
Automatic counting devices, such as loop detectors or radar-based systems, can be installed at entry and exit points of the roundabout to automatically record vehicle movements. Trained personnel or volunteers observe and manually record the number of vehicles entering, circulating within, and exiting the roundabout during specified time intervals.
Bicycle Count
Trained personnel or volunteers manually observe and record the number of bicycles passing a designated point during specified time intervals. Automatic Bicycle Traffic Counters are electronic devices installed along bike paths or roadways that use sensors to detect and record passing bicycles automatically. These counters can provide continuous data over extended periods, giving a more comprehensive understanding of bicycle usage trends.
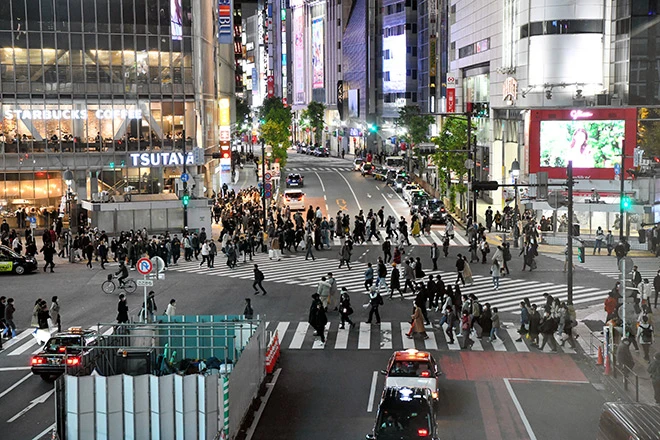


Pedestrian Count
Trained personnel or volunteers observe and manually record the number of pedestrians passing a specific point during designated time intervals. Automatic Pedestrian Traffic Counters are electronic devices installed at strategic locations that use sensors to detect and record passing pedestrians automatically. These counters can provide continuous data over an extended period, allowing for a more comprehensive understanding of pedestrian usage trends.
RTOR (Right Turn On Red)
Drivers must yield the right-of-way to any oncoming traffic, pedestrians, and cyclists before proceeding with the right turn. If there is a “No Right Turn on Red” sign posted at the intersection, drivers must not make a right turn on red. When making a right turn on red, drivers must be particularly cautious of bicyclists using the same lane or crossing the intersection.


ANPR (Automatic Number Plated Recognition)ETC
Automated toll collection systems use ANPR to identify vehicles and charge tolls electronically without the need for physical toll booths or toll attendants. ANPR is used by law enforcement agencies to identify vehicles that are involved in criminal activities or have outstanding violations. ANPR systems can be used to monitor parking lots and enforce parking regulations.
Origin Destination Surveys
These involve interviewing or surveying individuals or households to collect information on their travel behavior, such as trip purposes, destinations, modes of transport used, travel times, and frequencies of travel. License plate surveys use cameras or automated systems to capture license plate information of vehicles at various locations, such as intersections or parking lots, to determine the origin and destination of the vehicles.


Parking Surveys
Parking behavior surveys involve collecting data through interviews or questionnaires with parkers to understand their preferences, parking habits, and satisfaction. Modern technology, such as parking sensors, license plate recognition systems, and mobile apps, can provide real-time data on parking space availability and help optimize parking management.
Queue Length Counts
Queue length counts are typically conducted during peak traffic periods or at specific times of interest to capture the maximum queuing conditions. The surveyor identifies the intersection or traffic control point where the queue length count will be conducted. The location is usually chosen based on factors such as traffic volume, congestion, and importance to the transportation network. Identifying intersections or traffic control points with high congestion and prioritizing improvements.

Mapping
Traffic mapping relies on collecting relevant data about the movement of vehicles on roads. This data can be gathered through various sources, such as traffic cameras, sensors embedded in roadways, GPS devices, mobile apps, and even crowd-sourced data from users. This enables drivers to make informed decisions about their routes, avoid congested areas, and find alternative paths to their destinations.
Automatic Traffic Counts(ATC)
These are devices installed on the road or at intersections that use sensors, loops, or infrared beams to detect passing vehicles. Each time a vehicle passes over or through the sensor area, the counter records the count. RFID technology can be employed to track and identify vehicles automatically, allowing for traffic count data collection.